About Dowlatabad Garden
Dowlatabad Abad Garden is one of the sightseeing places of Yazd city, which is also considered as one of the world heritage of Iran and has been registered as one of the 9 Iranian gardens in the UNESCO World Heritage List. This beautiful garden, which is located in Chahar Minar neighborhood, is considered one of the oldest gardens in Yazd city.
Dowlatabad Abad Garden is one of the must-see places in Yazd and a UNESCO World Heritage Site in Iran. It is located on Shahid Rajaei Street in Chahar Minar neighborhood inside Ferdowsi or Hosseinieh Ferdous Alley and it is also accessible from Daulat Abad Boulevard. During the Qajar era, this garden was connected to the Chahar Minar gate, but it was still outside the city. But with the passage of time, the surrounding urban fabric filled it, so that during the Pahlavi period of construction, it covered the surrounding suburbs and gradually the garden was located in the center of Yazd city.
To see Daulatabad garden, travel to Yazd province and travel to Yazd city. After reaching this city, you can find this garden in Pamnar neighborhood. So go to Daulat Bad Boulevard and then Shahid Rajaei Street, in Hosseinieh or Ferdowsi Street is the place that houses Daulat Abad Garden.
History Of Dowlatabad Garden
Dowlatabad Garden of Yazd is one of the great gardens of Iran, which was built in 1747 during the Zandiye period. This large garden is one of the foundations and developments of Muhammad Taqi Khan, known as the Great Khan, the head of the Khawanin dynasty of Yazd and the powerful man of that era and contemporary with Shahrukh Mirza and Karim Khan Zand. Is. He first created an aqueduct named Dowlatabad and then created Dowlatabad Garden from the water of that aqueduct.
Dowlatabad garden size
Dowlatabad Garden is considered one of the most beautiful gardens in Iran, which is built in an area of about 4.6 hectares. During the time of Mohammad Taqi Khan, the garden reached a street with many trees from the north side; So that these trees blocked the view from the outside into the garden. For this reason, this street was also called a thousand trees, which was four to five meters wide and more than 20 kilometers long, and it went towards Rahim Abad. On the east side of the garden, there was an eight-kilometer street, and on the west side of the garden, it was limited to the channel of the dry river. At this time, the garden was located outside the city walls of Yazd.
Dowlatabad Garden aqueduct
The huge and important historical aqueduct of Dowlatabad Garden is more than two hundred years old, which consists of the construction of five series of aqueducts. This aqueduct plays an essential role in giving existence to Dowlatabad Garden, it is one of the most important and longest aqueducts of Yazd city with a length of approximately 60 km. The aqueduct originates from the heights of Mehriz and after draining a part of the land of Mehriz and putting some water mills into operation, it reaches Yazd and irrigates the entire garden of Dowlatabad Garden and then flows to the surrounding lands and irrigates the agricultural lands. .
Dowlatabad garden architecture
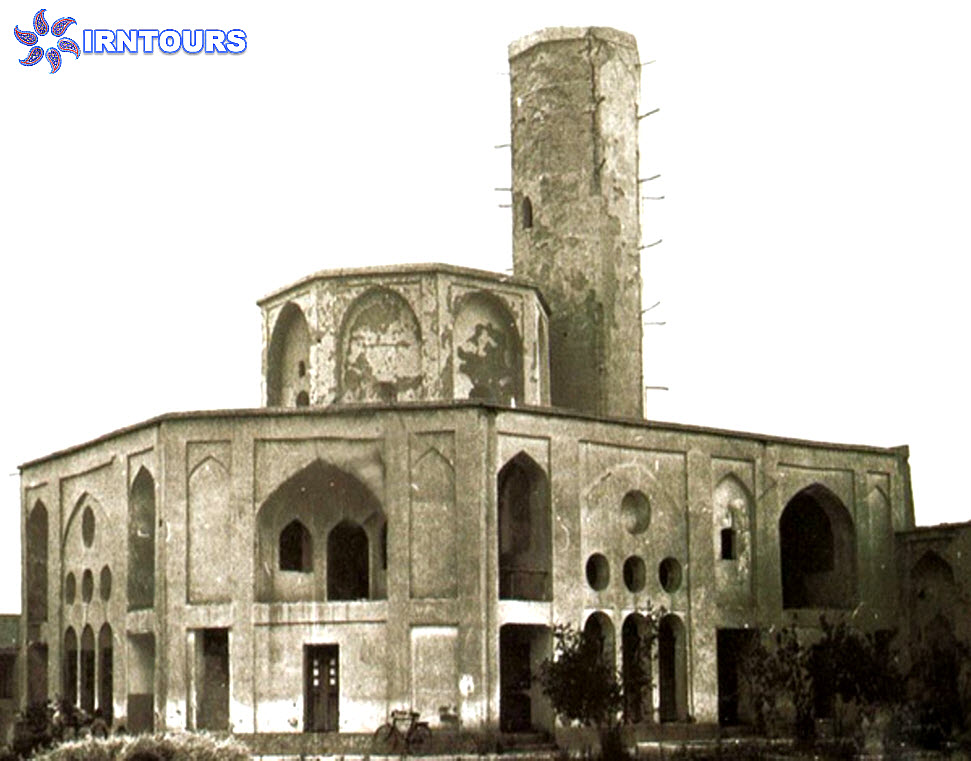
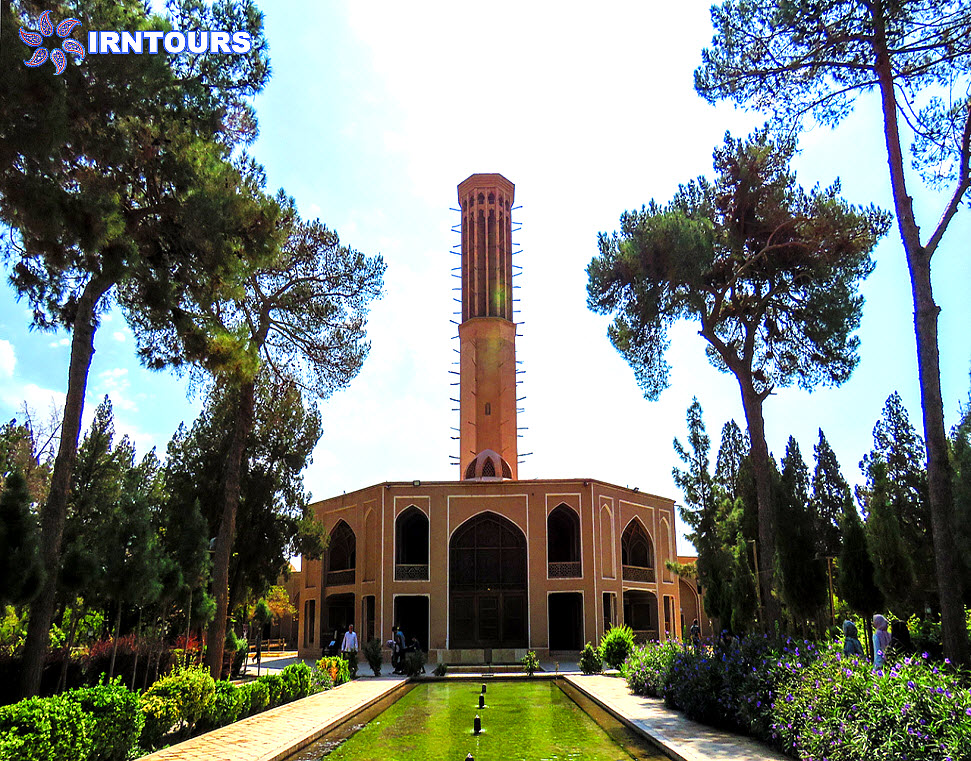
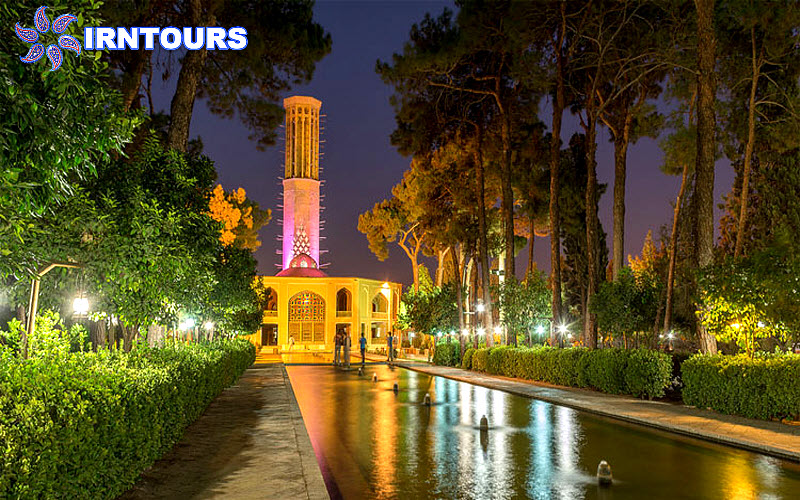
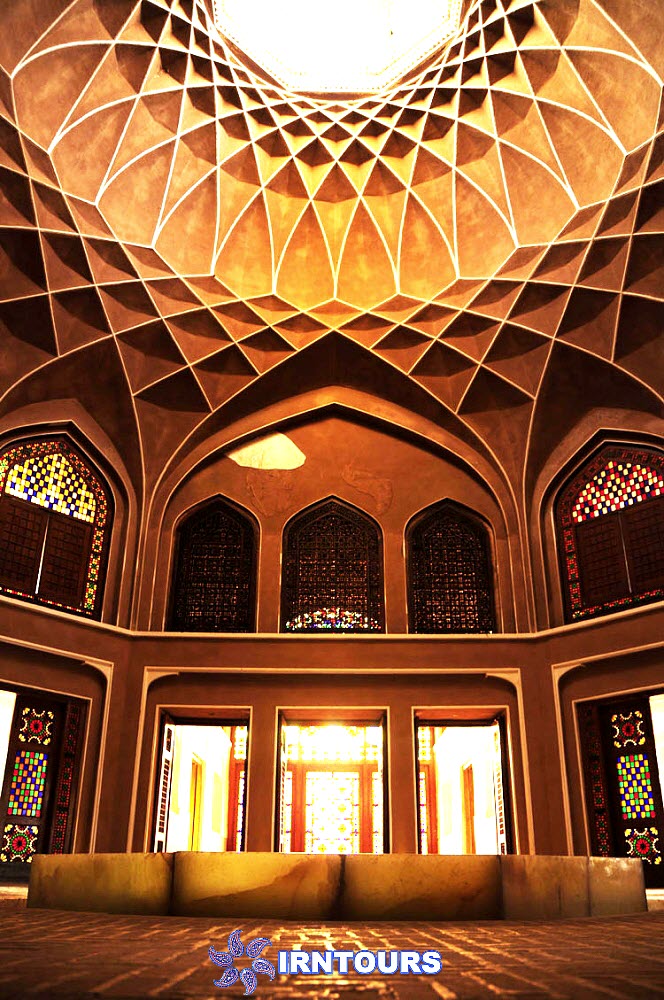
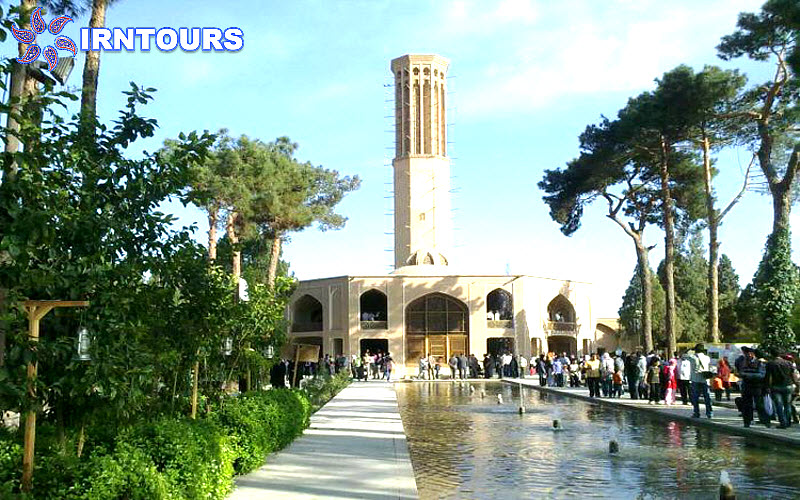
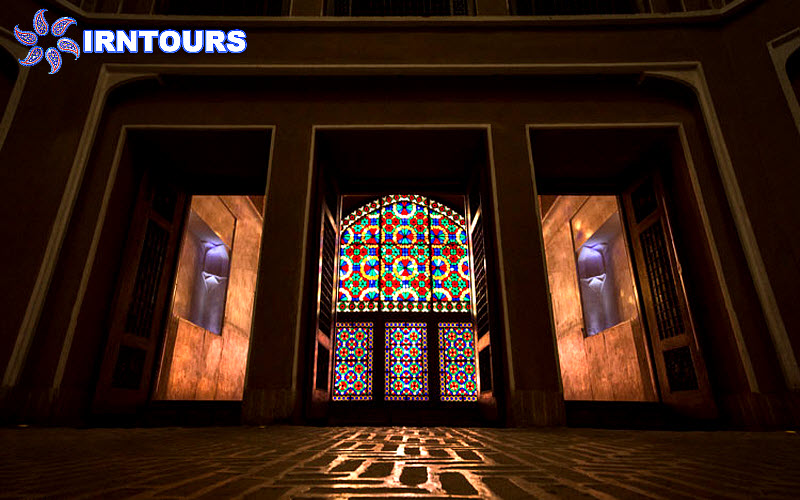
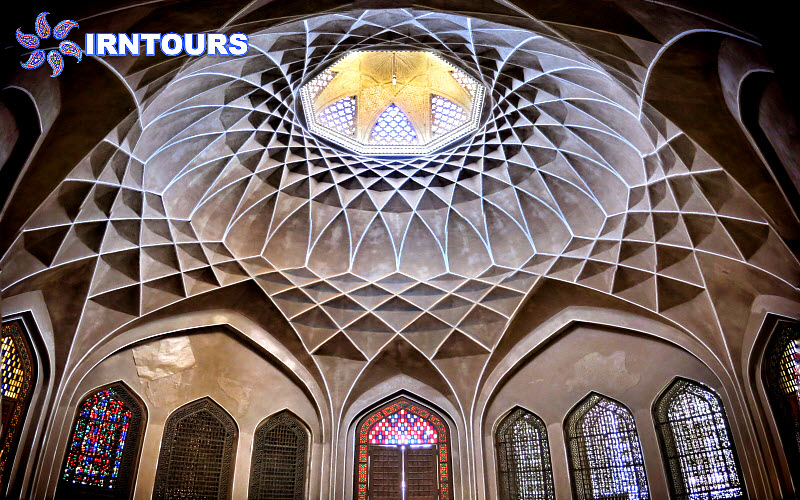
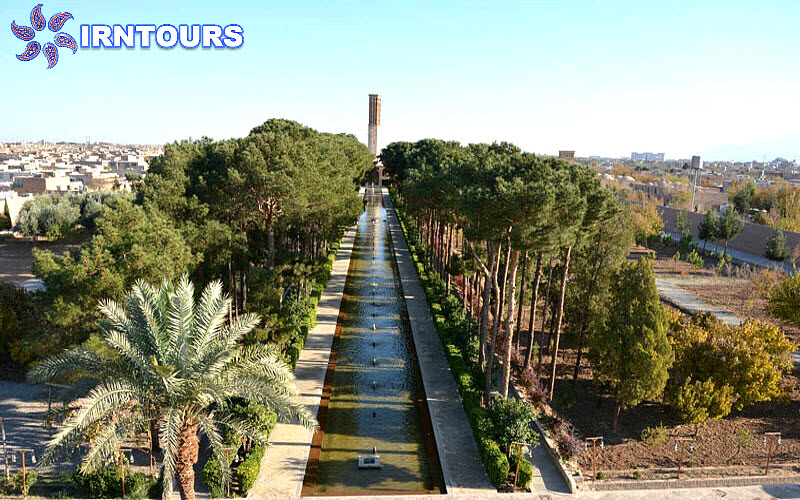
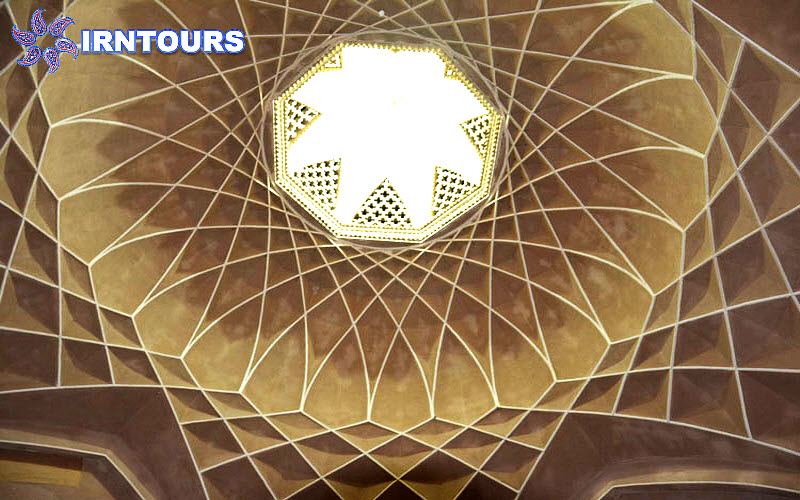
The tallest windmill in the world : What makes this garden stand out among Iranian gardens is its high windbreak, which is known as the tallest windbreak in the world with more than 8.33 meters. Another feature of this wind deflector is that it is octagonal, which makes the wind blow in any direction and is easily and quickly guided to the lower part. On the other hand, there is a pond under this wind trap so that by blowing the wind on the water surface of the pond, it creates cool air inside the building. In this building, with the combination of wind and water flowing in the pools inside the building, cool air is transferred from under the wind deflector to the king’s area and the halls. For this reason, this building is also called the summer building.
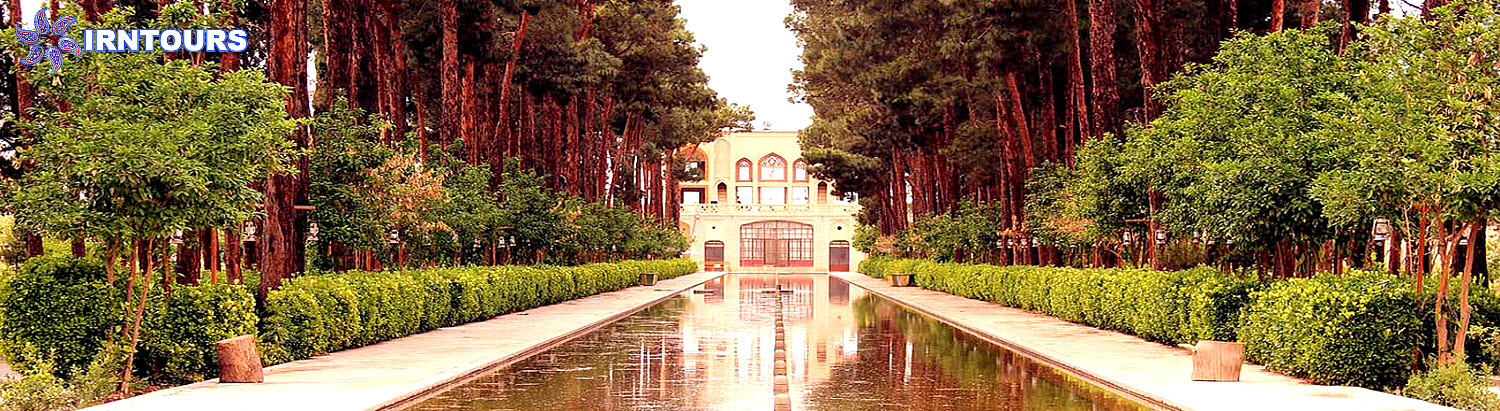
The geometry of the garden is very precise and it has separated the surface of the garden into two rectangular sections perpendicular to each other (the outer garden and the inner garden). The axis of symmetry of the bigger rectangle is the main axis of the inner garden, and the large water feature of the garden, measuring 194 x 12 meters, corresponds to this axis. In fact, this axis is the same axis that connects the Sardar mansion to the Hashti mansion. By planting trees on both sides of the main axis, the garden architect, in addition to focusing the view towards the main buildings of the garden, also causes the view of each building to be unrestricted towards the view of the garden and emphasizes the visual connection between the two buildings. The existence of the main landscape in a straight and elongated form in the longitudinal axis of the garden in front of the kiosk and planting tall trees on both sides of it play an essential role in creating a perspective that makes the garden appear longer. The fountain, which is exactly on the axis of symmetry of the inner garden, divides the garden surface into two symmetrical rectangular plots. In the inner garden, the main part of the garden is covered. The proportions of the plots follow the proportions of two rectangular gardens.
The symmetry axis of the smaller rectangle, which is the Garden of Beheshtayin, is perpendicular to the main axis of the garden. The rectangle of the Garden of Behesht Ayin is divided into two square parts by a large rectangular pond that is perpendicular to the axis of symmetry of the rectangle, which are actually the main plots of the Behesht Ayin Garden.
Symmetry is one of the principles of Iranian architecture, so it has been used in different forms in all buildings in traditional Iranian architecture. This principle is also used a lot in the Iranian garden. As the main building of the Iranian garden, the pavilion is placed on the symmetry axis of the garden. The peak of this symmetry can be seen in the main axis of the garden, where even flowers and trees are planted symmetrically. A noteworthy point in the geometry of Daulat Abad garden is the mismatch between the axis of the inner garden and the axis of the outer garden, so that the longitudinal axis of the inner garden deviates from the center of symmetry of the outer garden. In examining the cause of this problem, it seems that according to the time of the formation of the two gardens, which according to the available historical sources, both gardens were built at the same time or with a small time interval from each other, this discrepancy can be a basis for the next steps of research in the field. Daulat Abad garden geometry, which requires field research and search in relevant historical sources. Of course, the above assumption is made considering the older plans of the garden, because in the 1370s, with the construction of a large street in the north of the garden, a large part of Behesht Ayin Garden was destroyed and its land was used to build a boulevard.
Dowlatabad Abad garden design
Daulat Abad garden design is one of the most original and original Iranian official garden designs. The surface of the garden is divided into two sections with a rectangular perimeter with dimensions of 116 x 274 meters and 104 x 278 meters, which are stacked vertically. The axis of symmetry of the larger rectangle – the main axis of the garden – is located in the northwest-southwest direction with an angle of 30 degrees to the west-east axis. The larger rectangular area (what is now known to the public as Daulat Abad Garden) formed the interior garden, which was actually a private garden and family residence. The smaller rectangular perimeter, which is located on the north side, defines the boundary of the outer garden. This garden, which is called “Paradise Ritual” garden, has been the venue for government ceremonies and sports events.
Dowlatabad Abad garden buildings
The emergence of Daulat Abad garden buildings complex is after the construction and revival of the aqueducts that were formed with the same name and after the flourishing of the surrounding gardens, buildings including: Sardar Mansion, Behesht Ayan Mansion, Hall of Mirrors, Tehrani Mansion, Hasti Mansion or Badgir Mansion, Sardar Mansion North (related to Behesht Ayin garden), Tanbi hall, observation tower and water reservoir have been built. Also, a large stable with a camel house and a slave house is located in the west of the garden and next to the dry river. The green space of the garden has fruit trees such as grapes, cypress and pine, as well as Mohammedan and red flowers are also seen in the garden.
The collection of buildings in Dolat Abad, each one has architectural characteristics and original effects of the use of spaces needed at that time. In the following, you will get to know the three main buildings of this garden:
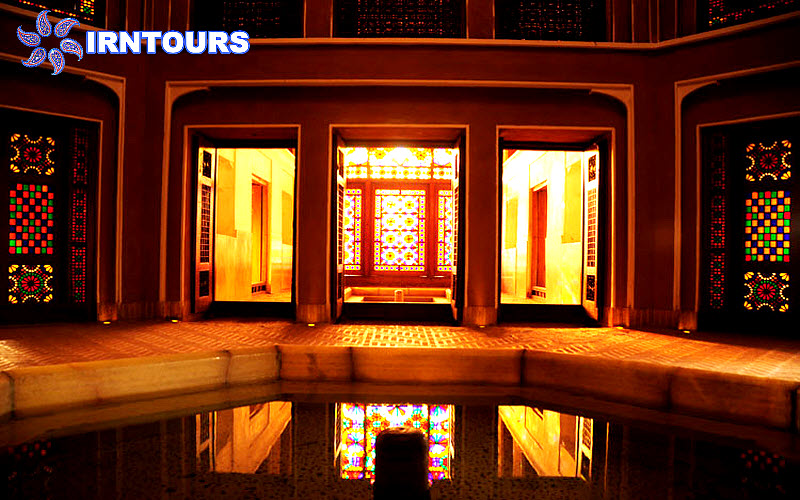
Hashti mansion: which is at the end of the main axis of the garden and connected to the south wall, is actually considered the main pavilion of the garden and has a special reputation due to its high windbreak. The Hashti mansion has three large rooms and a pool (with a single marble pool) in the middle. Its design is similar to other Iranian huts, and the upper floor has a hall, a row and a view.
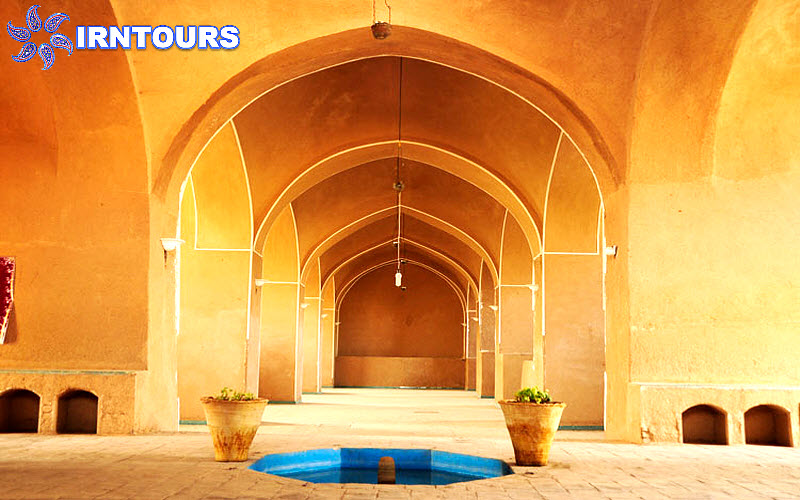
Tanbi Mansion: On the west side of the Hashti Mansion, there is a large and luxurious Tanabi Mansion, which has a square windbreak and faces the garden. On both sides of Tanbi Hall, there are halls, sefes and naves on the same floor, whose doors and openings open to Tanbi. Under the rope, a deep underground has been dug, which connects to the garden with two steps on the right and is connected to the area under the windbreak from the south side with a corridor.
Sardar Mansion: between the inner and outer gardens, the main mansion of Behesht Ayan Garden is considered to be two-story, and below it, there is a main hall, a vestibule, and a large room (facing east) and several small rooms (facing north and south) and There are several corridors.
In addition to these main buildings, there is a secondary and service building on the eastern side of the garden, including a water tank, a pantry, a kitchen, and well facilities and a water source with a gauro, which was used to fill the garden’s many ponds in times of water shortage.
Dowlatabad garden typology
Dolat Abad is a residential-government garden from the point of view of functional typology. In such a way that the outer garden was the place of government ceremonies, sports events and city administration, and the inner garden was the private and residential part of the complex. In residential-government gardens, the inner arena was completely distinguished from other arenas and even a gatekeeper or guard was assigned to supervise it.
From the point of view of physical typology, Daulat Abad is considered a garden-courtyard type because its buildings and buildings are located around the garden, such as Narenjestan Qavam and Haftenan Garden in Shiraz.
Dowlatabad garden irrigation system
The main source of water for the garden is Dolat Abad aqueduct. In addition to the aqueduct, for times of drought and to irrigate the garden and fill its many ponds, a well and a water source with a goro (what is called Gavro today) were built on the eastern side of the garden and next to the service building. Also, in emergency situations, they used the water stored in the garden reservoir.
In Daulat Abad garden, water is completely displayed. With an indescribable play, the architect has taken the water into and out of the ground many times, so that water is present on the entire surface of the garden. The water is first seen under the windbreak of the Hashti mansion and in a single marble pool where it boils and rises, then it enters a pool in the middle of this mansion and flows from it into three elongated rectangular pools in the three palaces. In front of the sash of the rooms, there are three marble chests, which are carved in a way to create a wave and show the volume of water more than it actually is.
The water from each Quebec chest enters a small pond called Hoz Kalgi and flows from there into the large water feature of the garden. This fountain is located exactly on the main axis of the garden, and its dimensions are proportional to the height of the Hashti mansion, so that the image of this mansion is completely reflected in the water. After that, the water enters Beheshtayin Garden from under the Sardar mansion and flows into a large 12-sided pool located in the north of the mansion, and from there it flows to three rectangular pools on the other three sides. Then the water flows from these pools to the streets and settlements and is used for cultivation. In fact, the architect was not satisfied only with the passage of water through the lower layers of the earth and watering the trees, but also brought the warm water to the ground and displayed it to water the souls of the desert dwellers as well.
Tips for Visiting Dowlatabad garden
- To visit Daulat Abad Garden and enjoy its beauty and pleasant atmosphere, you can visit this place every day from 7:00 AM to 10:30 PM (except Ashura Day).